Frequency settlement cluster
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Are you struggling to understand how to represent data using a visual representation? Have you heard of a Relative Frequency Bar Chart but aren’t sure what it means or how to use it effectively? Don’t worry, you’re not alone. In this post, we’ll dive into the world of Relative Frequency Bar Charts and explore their importance in representing data.
Data representation can be a daunting task for many individuals. It’s crucial to convey the data in a clear and concise way that can be easily understood by a wide audience. One-size-fits-all representation doesn’t exist, and choosing the wrong method can lead to incorrect conclusions. However, it’s essential to learn about different methods of representation, such as Relative Frequency Bar Charts, which can more effectively represent data in certain scenarios.
The target of a Relative Frequency Bar Chart is to represent the proportions of different values within a dataset. This chart shows how frequently different values appear in the data by showing the ratio of the frequency of each value to the total number of data points. Each bar in this chart represents a range of values, and the higher the bar, the higher the frequency of values within that range.
Relative Frequency Bar Charts aid in data representation by allowing the user to more accurately represent frequency visually. The user can also easily compare different proportions of values and gain insight into the distribution of data. Furthermore, it can be useful when working with larger datasets because it allows for better visualization of data trends at a glance.
Personal Experience with Relative Frequency Bar Chart
When working on a research project in college, I struggled to understand how to represent a large amount of data effectively. My professor recommended using a Relative Frequency Bar Chart, and I was amazed at how easy it was to comprehend the distribution of values within our dataset. The chart allowed us to identify trends and understand the data in a more meaningful way than we could have with just spreadsheets of numbers.
How to Create a Relative Frequency Bar Chart
To create a Relative Frequency Bar Chart, you first need to identify your dataset’s range. Then, divide the range into intervals and count how many data points fall within each section. Finally, calculate the proportion of data points in each interval to the total number of data points, and create a bar chart displaying this proportion for each interval. Make sure to label each axis and title your chart for clarity.
The Importance of Title and Axis Labels in Relative Frequency Bar Chart
Title and axis labels are essential components of any chart or graph, including a Relative Frequency Bar Chart. Without proper labeling, the audience may struggle to understand the information presented. The title should accurately convey the content displayed in the chart, and the axes should label the data and the frequency of values in the chart, respectively.
Choosing the Right Interval Size for a Relative Frequency Bar Chart
Interval size is essential when creating a Relative Frequency Bar Chart. It’s essential to choose an appropriate interval size that is large enough to capture meaningful data trends but small enough to distinguish differences between intervals. The optimal interval size varies depending on the dataset’s range and the data’s distribution. If the interval size is too large, it can obscure trends, while small intervals can create unnecessary clutter.
Conclusion of Relative Frequency Bar Chart
Relative Frequency Bar Charts are an essential tool for data representation. They allow the user to more accurately represent frequency visually, identify trends, and gain insight into the distribution of data. Creating a Relative Frequency Bar Chart requires identifying the dataset’s range, dividing it into intervals, and calculating the proportion of data points in each interval. Proper labeling and interval size are also crucial for effective representation in these charts.
Question and Answer
Q: When should I use a Relative Frequency Bar Chart?
A: Relative Frequency Bar Charts are effective for representing data that has a range consisting of multiple values with different frequencies. They can also be used for comparing the frequencies of different values across datasets.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating a Relative Frequency Bar Chart?
A: One common mistake to avoid is using an inappropriate interval size. It’s also essential to label the chart properly and ensure the audience can easily interpret the information displayed.
Q: Can a Relative Frequency Bar Chart display negative values?
A: Relative Frequency Bar Charts are not suitable for displaying negative values because the chart displays frequency as a proportion, and negative values cannot be scaled proportionately.
Q: How can I create a visually appealing Relative Frequency Bar Chart?
A: To create a visually appealing Relative Frequency Bar Chart, choose a color scheme that is easy on the eyes, use appropriate fonts and text size, and make sure the chart is clear and legible.
Gallery
Relative Frequency Graph Maker - MathCracker.com

Photo Credit by: bing.com / frequency relative graph maker bar chart frequencies
Chapter 2
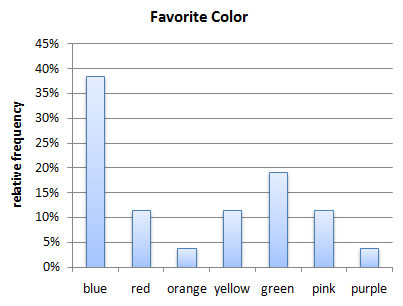
Photo Credit by: bing.com / bar frequency graph relative statistics technology graphs
PPT - Chapter 2: Descriptive Statistics PowerPoint Presentation, Free
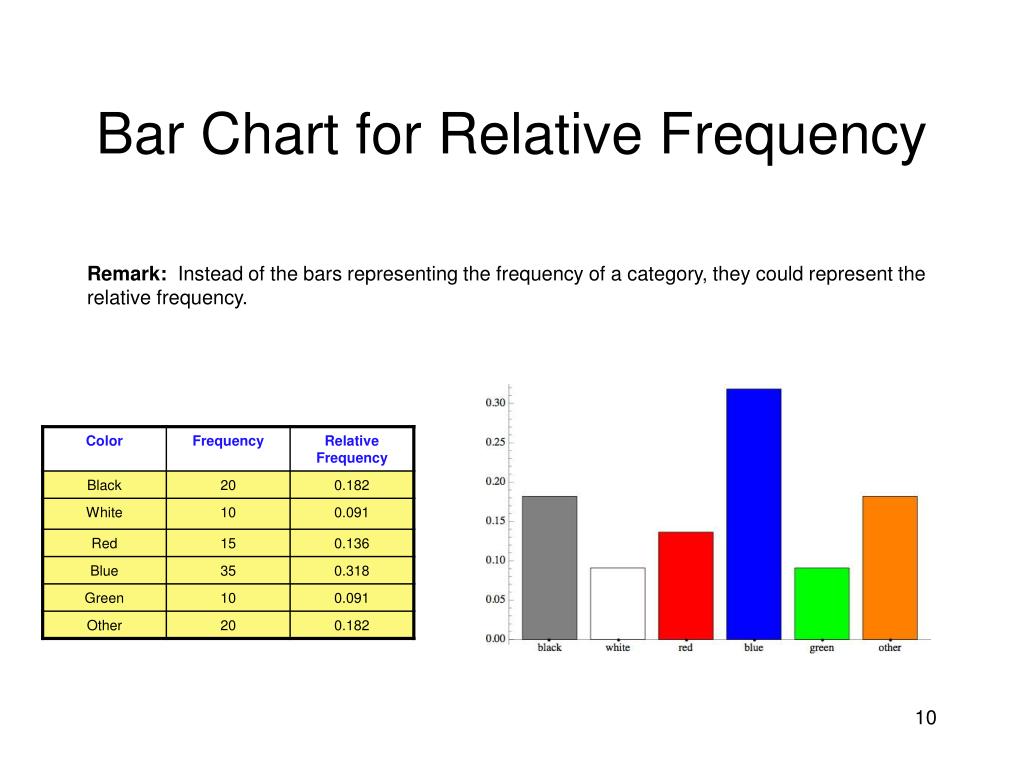
Photo Credit by: bing.com / frequency relative chart bar statistics descriptive presentation pie bars chapter ppt powerpoint
Relative Frequency Bar Chart Of Geomorphon Settlement Classification

Photo Credit by: bing.com / frequency settlement cluster
Relative Frequency Bar Chart Of Settlement Classification Per Cluster

Photo Credit by: bing.com /