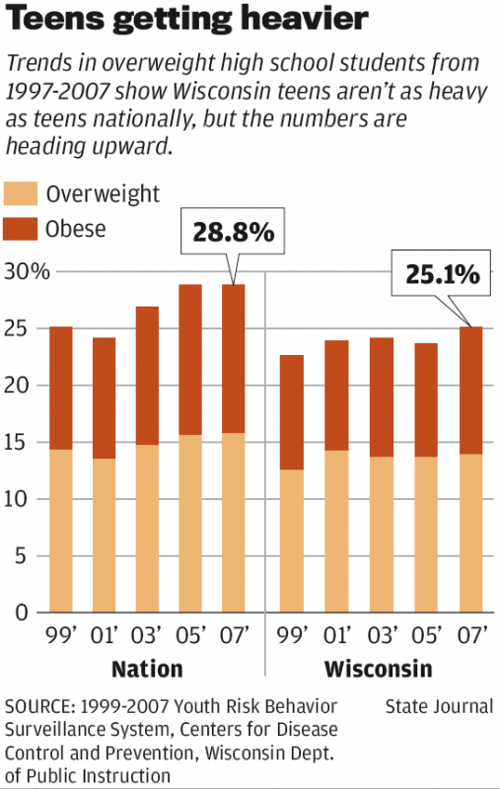
Histogram graph bar difference between teachoo last slide16
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
If you’re interested in data visualization, you may have come across the terms “bar chart” and “histogram” before. While they may seem similar at first glance, there are actually some key differences between the two. Understanding these differences is important if you want to effectively visualize and communicate your data.
Whether you’re working with marketing data, financial data, or any other type of data, chances are you’ll need to create charts or graphs at some point. Bar charts and histograms are two common types of charts used for visualizing data, but they serve different purposes and have different applications.
A bar chart is a graph that represents the data with rectangular bars, where the length or height of each bar is proportional to the value of the variable being plotted. Bar charts are used to compare different values or show changes in data over time. On the other hand, a histogram is a graph that represents the distribution of a continuous variable over a specified interval or time period. Histograms are used to show the frequency distribution of a dataset.
In summary, the main difference between a bar chart and a histogram is that a bar chart represents different categories of data while a histogram represents the distribution of a continuous variable.
Why Understanding the Difference Between Bar Chart and Histogram Matters
When you’re creating visualizations of your data, you need to select the right type of chart that will best fit your purpose and help you communicate your findings effectively. By knowing the difference between bar charts and histograms, you will be able to choose the right type of chart for your data and avoid potential misinterpretation of your results.
The Target of Bar Chart and Histogram Difference
One example of when it’s important to understand the difference between bar charts and histograms is when you’re working with data that is not continuous. For instance, if you’re working with data that is categorical, such as a survey that asks respondents to indicate their age range, you wouldn’t want to use a histogram, which is designed for continuous data. Instead, a bar chart would be more appropriate, since it allows you to easily compare the frequency of different categories.
On the other hand, if you’re working with data that is continuous and you want to show how the values are distributed over a given range, a histogram would be a better choice. For instance, if you’re analyzing the average height of a population, a histogram would provide a clear picture of the distribution of heights, such as how many people fall within a certain height range.
Bar Chart vs. Histogram Differences in Detail
Now, let’s take a closer look at some of the key differences between bar charts and histograms:
- Bar charts represent categorical data, while histograms represent continuous data.
- The bars in a bar chart can be arranged vertically or horizontally, while histograms always have bars that are vertical and adjacent to each other.
- In a bar chart, there is no space between the bars, while in a histogram there is a small space between adjacent bars to indicate the different ranges of the continuous variable being displayed.
- The bars in a bar chart can have different widths, while the bars in a histogram need to be uniform in width to represent the intervals or ranges of the continuous variable.
- A bar chart can have any number of bars, while a histogram typically has between 5 and 15 bars to represent the distribution of the continuous variable in a meaningful way.
When to Use Bar Charts vs. Histograms
To summarize, if you want to compare different categories or values over time, a bar chart is the appropriate choice. On the other hand, if you want to show the distribution of a continuous variable over a range of values, a histogram is the way to go. In general, it’s a good idea to choose the chart type that best suits your data and your goals for visualizing it.
Question and Answer Section
Q: Are there any differences in the type of data required to create bar charts and histograms?
A: Yes, there is a difference. Bar charts are typically used for categorical data, while histograms are used for continuous data.
Q: Can you use a histogram to compare data points?
A: No, histograms are designed to show the distribution of a continuous variable over a range of values, not to compare individual data points.
Q: What is the main purpose of a bar chart?
A: The main purpose of a bar chart is to compare different values or categories of data.
Q: How do you determine the optimal number of bars for a histogram?
A: There is no hard and fast rule for determining the optimal number of bars for a histogram. Typically, you want to have enough bars to accurately represent the distribution of the data, but not so many that it becomes difficult to understand the chart. A common rule of thumb is to use between 5 and 15 bars.
Conclusion of Bar Chart Histogram Difference
Bar charts and histograms are two commonly used types of charts for visualizing data, but they serve different purposes. Understanding the difference between the two is essential if you want to create effective visualizations of your data. By selecting the right type of chart, you can avoid misinterpreting your results and communicate your findings more clearly.
Gallery
Histograms | Solved Examples | Data- Cuemath

Photo Credit by: bing.com / histogram bar difference histograms data graph chart between examples differences calculate these
What Is The Difference Between A Histogram And A Bar Graph? - Teachoo

Photo Credit by: bing.com / histogram teachoo subscribe
8 Key Differences Between Bar Graph And Histogram Chart | Syncfusion
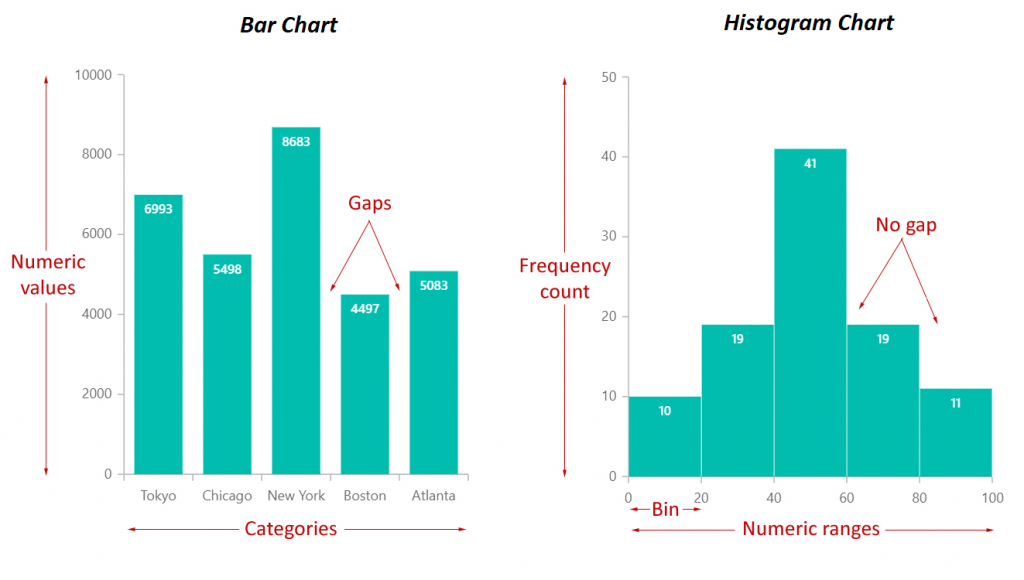
Photo Credit by: bing.com / histogram syncfusion difference axis
What Is The Difference Between A Histogram And A Bar Graph? - Teachoo

Photo Credit by: bing.com / histogram graph bar difference between teachoo last slide16
What Is The Difference Between A Bar Graph And A Histogram [Solved]
![What Is the Difference Between a Bar Graph and a Histogram [Solved] What Is the Difference Between a Bar Graph and a Histogram [Solved]](https://d138zd1ktt9iqe.cloudfront.net/media/seo_landing_files/screenshot-2021-03-01-at-9-17-06-am-1614570481.png)
Photo Credit by: bing.com / histogram bar between graph difference differences chart basic thus seen